12 May Links, AI and Google May 2020 Update via @martinibuster
Some in the SEO community have noticed linked related patterns in sites that have lost rankings. Is there anything to it?
Yesterday, Jeff Coyle (@jeffrey_coyle) of MarketMuse (@MarketMuseCo) shared results of his research and noted that sites with a high rate of link acquisitions were winners in the local search space.
He also noted that thin pages that were supported by off-page factors like links were also suffering, as if those links were no longer helping.
It’s good to be aware of the change. But it’s prudent to not make assumptions based on that knowledge.
Jeff did not say that those were the reasons for the changes. What he described were unusual patterns.
Google Nofollow Hint Changed March 2020
Something to keep in mind is that March 1, 2020 is the date that Google was supposed to begin using Nofollow as a hint for crawling and indexing purposes.
According to Google’s official announcement in September 2019, Google was already using nofollow as a hint for ranking purposes.
A further change was set to happen in 2020. We’re now two months past that date when a change in crawling and indexing has happened.
Is there a connection? Google has not confirmed any connection.
Link Acquisition Rates and Update Losers
The founder of Link Research Tools (@lnkresearchtool), Christoph Cemper (@ChristophCemper), shared an interesting observation.
He posted on Facebook that he was seeing a pattern in many sites that had lost rankings.
What he saw was sites with a negative link velocity losing rankings.
Link velocity is a phrase that describes the rate at which a site acquires links.
A negative link velocity trend is the situation when a site is actually shedding links, where links are dropping off.
Every site loses links. But if a site is relevant then they are also acquiring links. An active and popular site will naturally acquire more links than they lose.
What Christoph Cemper saw was that sites that were losing links at a rate that resulted in a net loss of links were losing in this latest update.


It’s an interesting observation that sites with negative link velocity would be big losers. In my opinion the link velocity may be a quality of the kind of site that would lose rankings.
But in my opinion, the link velocity itself is probably not the cause of the loss in rankings. The cause of the loss in rankings might have something to do with why a site has become irrelevant to Internet audiences.
The questions I would ask is, why aren’t sites no longer linking to these loser sites?
Pandemic Disruption to Search Trends
The question of why nobody is linking to a site is more complicated to answer at this time, because of the pandemic.
For example, many of the big losers in the update were gyms, like Planet Fitness.
Less people might be linking to gyms because gyms are less relevant to people at this moment in time.
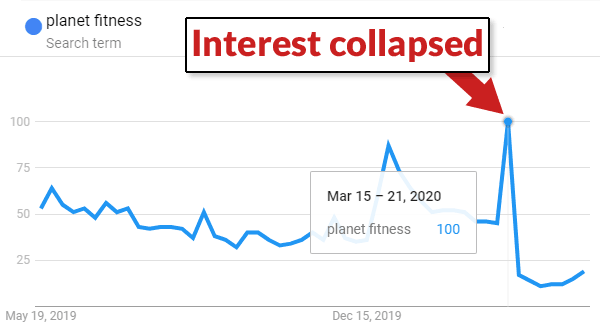

I have my doubts that the linking patterns are the cause. They may simply be a coincidence of this moment in time.
Fact: Pandemic Can Disrupt AI
MIT Technology Review recently published news that the Covid-19 pandemic has disrupted the search patterns that AI systems are trained on. MIT says that this has resulted in AI algorithms returning bad results.
According to the MIT article:
“Machine-learning models are designed to respond to changes. But most are also fragile; they perform badly when input data differs too much from the data they were trained on.”
It’s a thought provoking scenario. Is it possible that Google’s algorithm was updated to respond better to search trends? Or is Google’s algorithm itself affected from the changed “input data?”
Negative SEO
Nobody checks their backlinks for issues when the rankings are fine. Why fix something that’s not broken, right?
It’s when things go wrong that a publisher pokes around in their backlinks looking for answers. And that’s when many publishers are shocked to discover that spam sites have been linking to them with some truly low quality links.
Some sites may actually begin to rank for adult related keywords.
The reality however is that it is highly unlikely that those spammy links are related to losses during a Google update.
I have had many publishers who were Google Update casualties come to me after having disavowed thousands of low quality links. The links were never the reason why they had lost rankings. The money they spent on disavowing links had been wasted.
The answers to why a site lost rankings, in my opinion, were always due to other factors that had nothing to do with negative SEO.
Google’s John Mueller recently asserted that negative SEO is not a ranking issue.
Not to put more fuel on the fire, but negative SEO is not a reason we have this tool — and I honestly can't recall a situation where a site ever needed to do a disavow for that. I'm sure there are a handful of cases, but for the most part, it's totally unnecessary time spent.
— 🍌 John 🍌 (@JohnMu) May 12, 2020
A publisher who has suffered a setback during Google’s May 2020 Update should not assume that negative SEO is to blame.
First, wait another week or so for rankings to stabilize. If rankings do not return then the answer is elsewhere.
Takeaways
When diagnosing Google algorithm update ranking problems, it’s important to not make assumptions based on correlations that may be visible, particularly when it comes to links.
Broad Core Updates are so-called because they are many changes to different parts of the algorithm. One part might be links. Another part might be related to natural language processing.
The thing that you see as a cause might only be a quality of the site and not the reason for a ranking drop.
Citation
MIT Technology Review Article
Our weird behavior during the pandemic is messing with AI models
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.