14 May Naver SEO: Best Practices for South Korea via @TaylorDanRW
Only in a small handful of locations is Google’s dominance challenged to a meaningful extent, and of those such locations is South Korea.
Depending on your source, it’s estimated that Google holds between 70% and 85% of the South Korean search market, with challenger and South Korean native search engine Naver holding between 15% and 30%.
In the mix as well, but at much lower percentages, are Baidu, Daum (another South Korean native), Bing, and DuckDuckGo.
Regardless of market size, Naver is used by South Koreans not only for its search functionality but for its other products, meaning that entering the market with a Google-only search strategy will limit your potential audience reach.
Naver’s SERPs
A key difference between Google, Bing, Yandex, and Naver, as well as Baidu and Daum, is their self-titled definitions. The former describe themselves as search engines, whereas the latter describe themselves as web portals.
Similar to NetScape in the 1990s, they are directories designed to act as gateways to other content, often removing the need for users to conduct their own searches.
And when a user does conduct their own search on Naver, they don’t always get organic results.
Searching for a generic keyword like “marketing” (마케팅), we typically get the following above the fold on desktop:
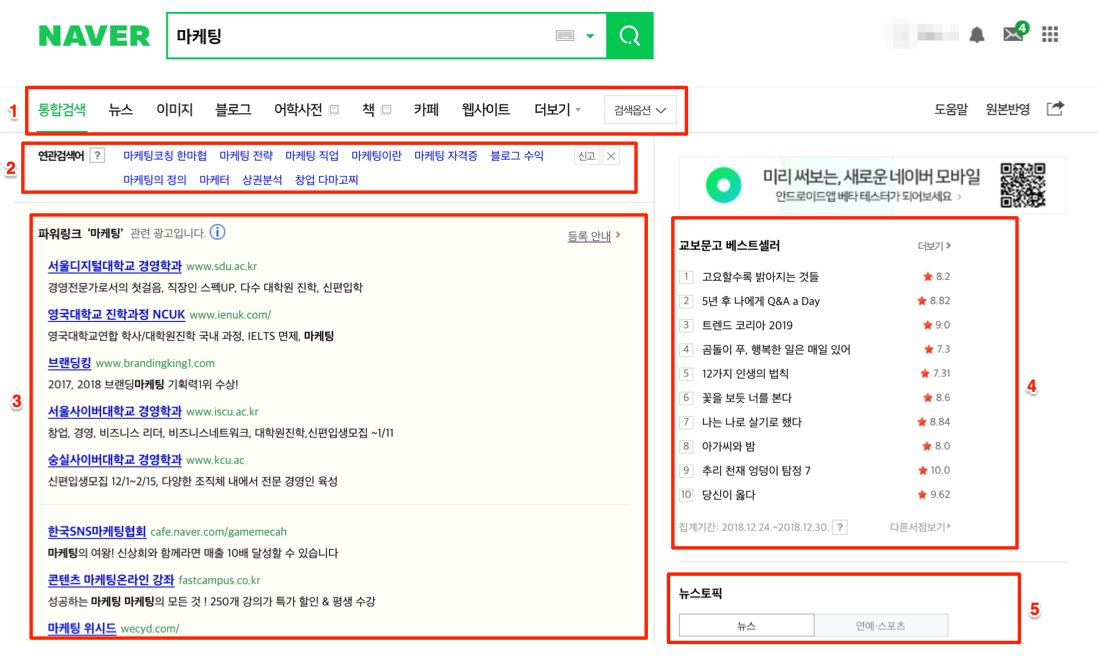

- Vertical searches – linking to results on Naver Knowledge iN, Café, Blog…
- Related search terms
- Paid search ads – clearly distinguished by their colored background
- Related books that have been released recently
- Current news topics relating to the query
The SERP layouts change a lot depending on the query, as Naver (like Google) is able to:
- Recognize entities, brands, and trending topics.
- Pull information from other websites into the search results pages to satisfy user intent there and then. An example of this is searching for Daegu FC (a South Korean soccer team):
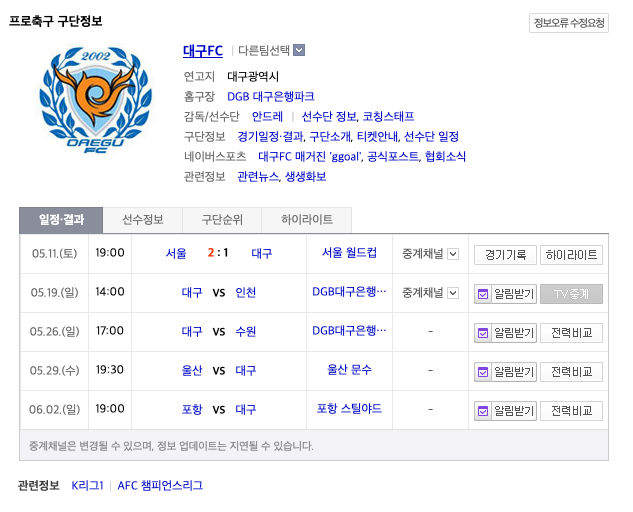
 A special Naver SERP feature for K-League soccer team Daegu FC
A special Naver SERP feature for K-League soccer team Daegu FCLike Google, there is no accreditation to the information source – and if you want to search for another soccer team, you can select a drop down from this search feature and select another team to update the SERP and results.
Naver Products
Much like Baidu and Yandex, Naver has a portfolio of products that both attract users, act as components within its SERPs, and influence organic ranking.
The primary products that you need to include in your strategy are:
Naver Encyclopaedia
Similar to Wikipedia, but a lot less restrictive in terms of setting up branded pages. If you’re new to the South Korean market, setting up a brand page here is a must.
Knowledge iN
Similar to Yahoo Q&A and Quora, the Knowledge iN takes in data from a number of sources (including its own) and can be prominent in search results – especially for interrogative searches.
Naver Blog
When you set up a Naver Webmaster Tools account you automatically get a Naver Blog.
While blogging and content marketing is important to Google, with Naver it’s important you blog on both your own website and the third-party Naver site.
Naver Café
Similar to Reddit and Baidu Tieba, Café is a community-based platform that brings together members with a common interest for sharing knowledge and engaging in discussion on that topic.
Naver’s Ranking Factors & Algorithms
Given Naver’s lack of exposure outside of South Korea, not a lot is known about the various algorithms that govern the search engine and its rankings.
However, we know of two core algorithms known as C-Rank and P-Rank.
C-Rank Algorithm
The C-Rank algorithm, also known as the Creator Rank, focuses on signals generated via Naver’s other products, such as the Naver Blog and Naver Café, and the user-generated content within.
Through C-Rank, Naver attempts to establish the authority, popularity, and reliability of content being shared on the Blog, Knowledge iN and Café, versus website produced content.
| Product | Ranking Factors Considered |
| Naver Blog |
|
| Naver Café |
|
| Naver Knowledge iN |
|
P-Rank Algorithm
P-Rank was introduced by Naver to make its organic results “higher quality”, to better match the standards set by other search engines such as Yandex and Baidu.
Using a form of artificial intelligence data processing, Naver processes a number of ranking factors in order to ascertain the relevance of a webpage with a search query, as well as the quality of the webpage itself.
In short, these criteria can be summarized as:
- Website crawlability and accessibility by Naver Bot.
- The level of on-page optimization and on-page meta data.
- The website structure and internal linking.
- Mobile usability.
- The number of, and quality of backlinks pointing to a website.
- Social media signals.
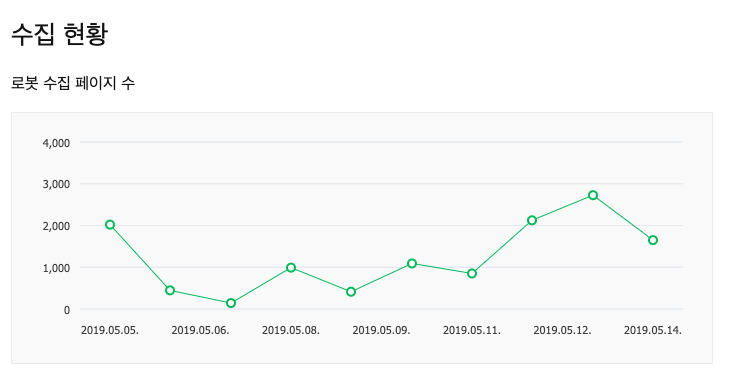
 The crawl status of a website within Naver WMT – the number of pages NaverBot is “collecting” daily
The crawl status of a website within Naver WMT – the number of pages NaverBot is “collecting” dailyOther Ranking Factors
I’ve worked with a number of clients to help expand their SEO strategy to South Korea.
From experience (and reading a number of other case studies and comments on Naver forums), the below ranking factors are not confirmed – but they are correlative:
CTR & Other SERP Signals
Naver monitors and collects data on how users behave on SERPs, much like Google.
How much does this affect organic ranking positions (given the often lack of organic results on a Naver SERP)? The impact is negligible.
Keyword Usage & Frequency Within Content
While Google has made great strides in understanding user intent and understanding entities, often called semantic search, Naver works in a more basic fashion.
Naver looks for the target keywords and their associated variants.
Content Freshness
The time decay factor is a lot more prominent within Naver than it is with Google.
This means that evergreen content pieces do require regular maintenance and it’s important that you produce content and blog both natively as well as via Naver Blog.
More Resources:
- The Best Practices of Optimizing for International SEO
- How to Use Hreflang for a Multilingual Website
- Top-Level Domain & Other Restrictions for International SEO
Image Credits
All screenshots taken by author, May 2019
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.